페이지 위치
Gastroscopy
- Exam. Time :30mins (including pretreatment)
- Price :90,000 won (except for 40,000 won for conscious sedation) * apply separately for conscious sedation.
※ Additional costs may apply for biopsy and polyp removal surgery.
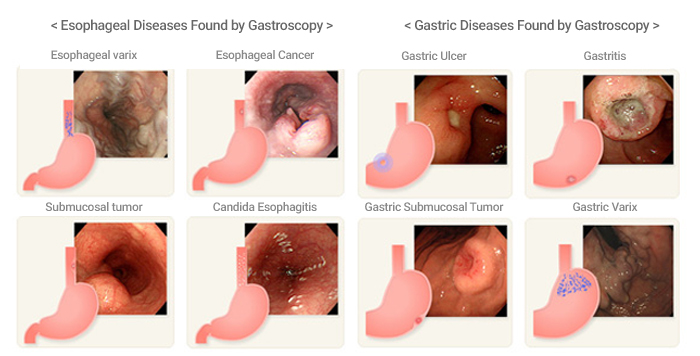
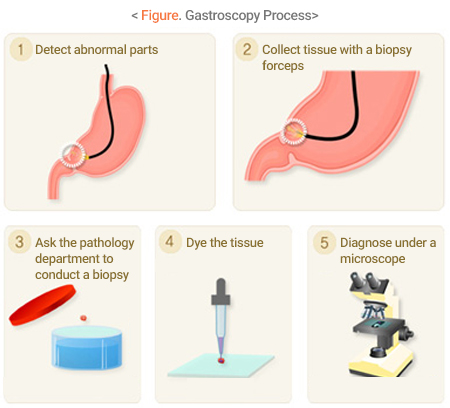
A gastroscopy is to evaluate the shape, size, and location of gastric cancer by observing the inside of the stomach directly through the endoscope, and conduct a biopsy in the suspected area. This is required to confirm the gastric cancer through a biopsy, to determine the scope of the operation, and to find the early gastric cancer without symptoms.
Recently, a dye is used to paint mucous membranes or immunofluorescence is injected to improve the accuracy of diagnosis.
An examinee must fast from the previous night, take medications to remove air bubbles and mucus in the stomach just before the examination,
and keep local anesthetic in the mouth for about five minutes to reduce discomfort caused when inserting an endoscope.
The upper endoscopy takes about 5 to 10 minutes, and if the endoscopy causes great anxiety, a conscious sedation (sedative) gastroscopy is recommended.
As the sedative gastroscopy is carried out after injecting a sleeping- inducing sedative, the patient can be examined more comfortably than normal gastroscopy due to the antianxiety or anterograde amnesia effects (memory loss effects).
However, as the patient is not unconscious or anesthetized, the patient can cooperate during the examination.
In addition, despite the appropriate amount of medication used, some people fail to fall asleep or be under conscious sedation, and in some cases, the examination can be difficult due to the lack of cooperation from the patient.
The sedative gastroscopy is relatively safe, but caution is req uired for the elderly or those who have deteriorated cardiopulmonary functions.
1. Examination Method
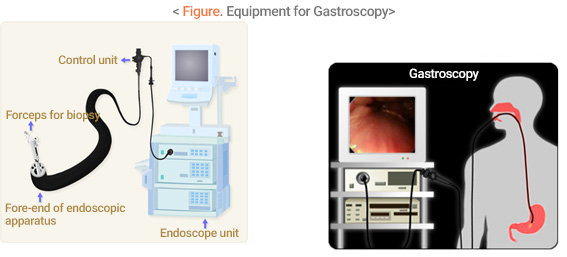
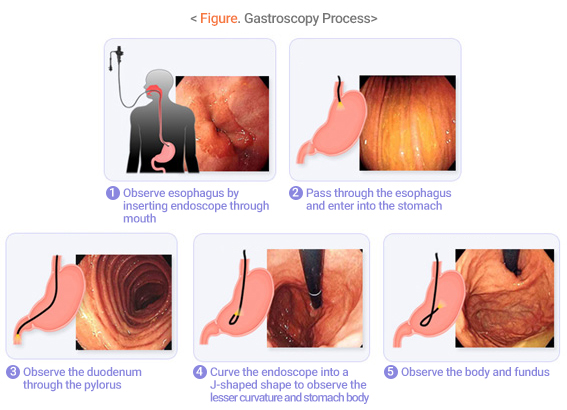
- When the endoscope which is inserted into the mouth via the mouthpiece hole passes through the neck to the esophagus, stomach and duodenum, the examiner can observe the esophagus, stomach, and
- duodenum mucosa directly.
- Sometimes you feel pressure, nauseated, or mild pain when the equipment goes through your neck, but after that, you have little pain.
- It is relatively easy to insert the endoscopy as you relax your tongue and neck, breathe deeply with your nose and belly, and then suppress your cough.
- After then, breathe with your abs slowly, bear vomiting and avoid swallowing the saliva in your mouth.
- Sometimes a biopsy can be conducted to diagnose esophageal, gastric, or duodenal abnormalities found during an examination.
- Cancer is not always suspected when conducting a biopsy as even minor inflammation may be examined for accurate diagnosis.
- The examination will take approximately 10-15 minutes, but in some cases it may take longer.
2. Possible Complications with Gastroscopy
- The gastroscopy for diagnosis is a safe examination commonly conducted by medical institutions, but it rarely accompanied with complications.
- Various medications used for the endoscopy can result in allergic reactions such as urticarial and asthma, or complications in the heart system such as arrhythmia or myocardial infarction.
- In addition, the examination may lead to bleeding, abdominal pain, perforation
- Temporary fever or sepsis within hours after the examination, temporary swelling of the parotid region and pressure ache. But in most cases these symptoms do not continue.
3. Possible Complications with Sedative Gastroscopy
- Complications in respiratory system complications such as dyspnea and hypoxia
- Complications in cardiovascular system, such as brachycardia or decreased blood pressure
- Falling
- In rare instances, the examination can lead to life-threatening situations such as respiratory standstill, or cardiac arrest and first aid may be required due to hypersensitivity reactions. Therefore, those who have respiratory problems or kidney or heart problems should be careful when receiving a sedative endoscopy.
- After a sedative endoscopy, you need to take a rest for complete recovery. On the day of the examination, you should not drive and avoid making important appointments or doing tasks.
4. Cautions after Examination
- Do not eat food for up to 30 minutes after the examination.
- If you have a biopsy, start eating about two hours after the examination.
- If you eat food before the anesthesia wears off, the food may go down the wrong pipe and cause aspiration pneumonia.
- Sometimes, a pain in the neck persists after the anesthesia wears off, but you don't have to worry about it as it's usually temporary.
- In such cases, drinking lukewarm water or rinsing your throat can help relieve the pain.
- You may find the saliva in a small amount of blood, but in most cases it is temporary.